In its simplest form, a wide-area network (WAN) is a collection of local area networks (LANs) or other networks that communicate with one another. A WAN is essentially a network of networks, with the Internet the world's largest WAN.
These networks are often established by service providers that then lease their WAN to businesses, schools, governments or the public. These customers can use the network to relay and store data or communicate with other users, no matter their location, as long as they have access to the established WAN. Access can be granted via different links, such as virtual private networks (VPNs) or lines, wireless networks, cellular networks or internet access.

.png?width=80&height=80&name=Blank%20100%20x%20100%20(19).png)
.png?width=80&height=80&name=Blank%20100%20x%20100%20(20).png)
.png?width=80&height=80&name=Blank%20100%20x%20100%20(24).png)
.png?width=250&height=123&name=Etsy%20Shop%20Owner%20Photo%20(9).png)
.png?width=250&height=123&name=Etsy%20Shop%20Owner%20Photo%20(22).png)
.png?width=250&height=123&name=Etsy%20Shop%20Owner%20Photo%20(25).png)
.png?width=250&height=123&name=Etsy%20Shop%20Owner%20Photo%20(23).png)
.png?width=250&height=123&name=Etsy%20Shop%20Owner%20Photo%20(15).png)
.png?width=250&height=123&name=Etsy%20Shop%20Owner%20Photo%20(13).png)
.png?width=250&height=123&name=Etsy%20Shop%20Owner%20Photo%20(26).png)
.png?width=250&height=123&name=Etsy%20Shop%20Owner%20Photo%20(10).png)
.png?width=250&height=123&name=Etsy%20Shop%20Owner%20Photo%20(16).png)
.png?width=250&height=123&name=Etsy%20Shop%20Owner%20Photo%20(19).png)
.png?width=250&height=123&name=Etsy%20Shop%20Owner%20Photo%20(12).png)
-1.png?width=250&height=123&name=Etsy%20Shop%20Owner%20Photo%20(7)-1.png)
.png?width=250&height=123&name=Etsy%20Shop%20Owner%20Photo%20(28).png)
.png?width=250&height=123&name=Etsy%20Shop%20Owner%20Photo%20(8).png)
.png?width=250&height=123&name=Etsy%20Shop%20Owner%20Photo%20(11).png)
.png?width=250&height=123&name=Etsy%20Shop%20Owner%20Photo%20(17).png)
.png?width=250&height=123&name=Etsy%20Shop%20Owner%20Photo%20(21).png)
.png?width=250&height=123&name=Etsy%20Shop%20Owner%20Photo%20(24).png)
.png?width=250&height=123&name=Etsy%20Shop%20Owner%20Photo%20(27).png)
.png?width=250&height=123&name=Etsy%20Shop%20Owner%20Photo%20(20).png)
.png?width=250&height=123&name=Etsy%20Shop%20Owner%20Photo%20(18).png)
.png?width=250&height=123&name=Etsy%20Shop%20Owner%20Photo%20(7).png)
.png?width=250&height=123&name=Etsy%20Shop%20Owner%20Photo%20(14).png)
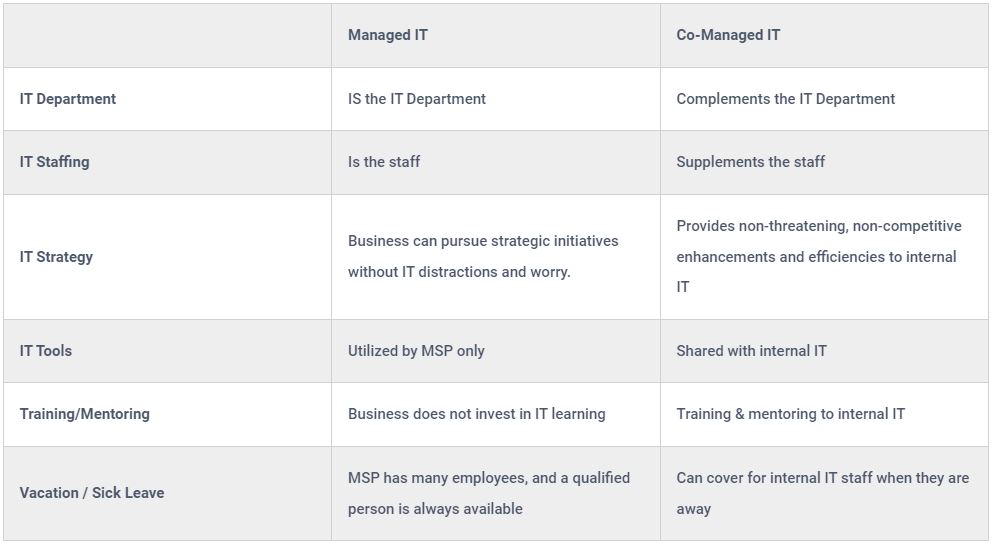

.png?width=450&height=385&name=Facebook%20Post%20(1).png)

.png?width=60&height=60&name=images%20(18).png)
-1.png?width=60&height=60&name=images%20(16)-1.png)